What is Industry 4.0 and what are some of the technologies that are driving it? Industry 4.0 is a term that refers to the fourth industrial revolution, which is characterized by the integration of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, big data, the internet of things, robotics, and 3D printing, into the manufacturing sector. Industry 4.0 aims to create smart factories that are more efficient, flexible, and responsive to customer needs and market changes. Some of the technologies that are enabling Industry 4.0 are: - Artificial intelligence (AI) : AI is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, decision-making, and problem-solving. AI can help optimize production processes, improve product quality, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. - Cloud computing: Cloud computing is delivering computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, software, and analytics, ov...
Debounce
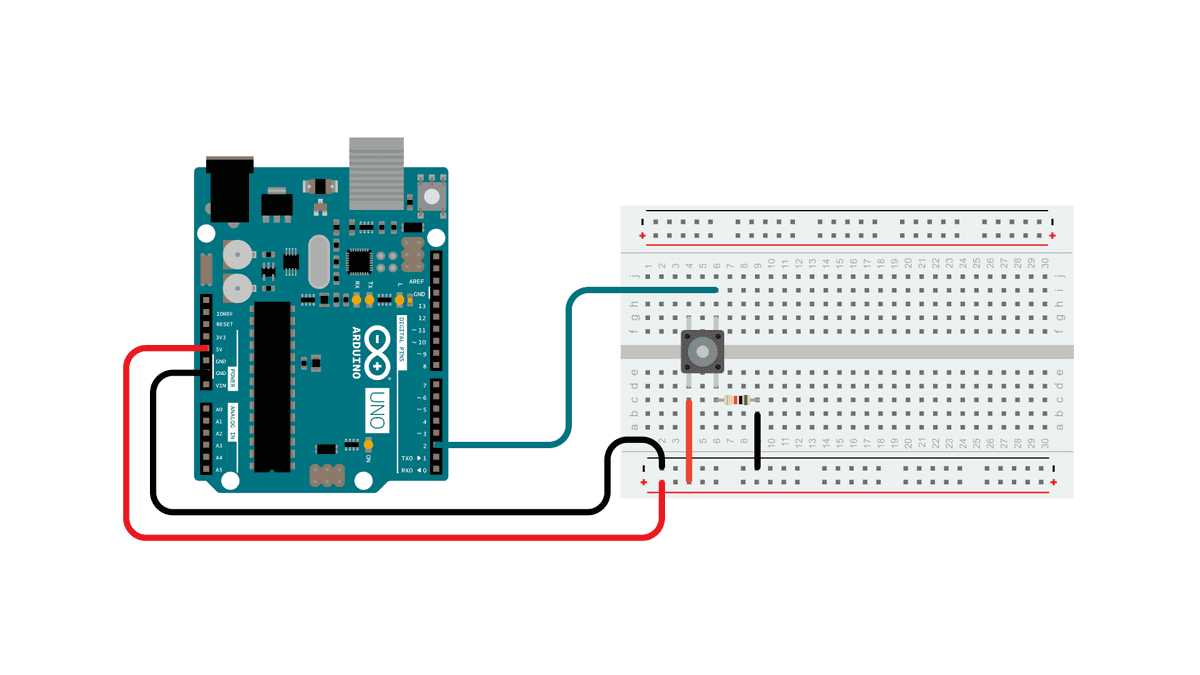
Pushbuttons often generate spurious open/close transitions when pressed, due to mechanical and physical issues: these transitions may be read as multiple presses in a very short time fooling the program. This example demonstrates how to debounce an input, which means checking twice in a short period of time to make sure the pushbutton is definitely pressed. Without debouncing, pressing the button once may cause unpredictable results. This sketch uses the millis() function to keep track of the time passed since the button was pressed.
Hardware Required
Arduino Board
momentary button or switch
10k ohm resistor
hook-up wires
breadboard
Circuit Diagram
Code
// constants won't change. They're used here to set pin numbers:
const int buttonPin = 2; // the number of the pushbutton pin
const int ledPin = 13; // the number of the LED pin
// Variables will change:
int ledState = HIGH; // the current state of the output pin
int buttonState; // the current reading from the input pin
int lastButtonState = LOW; // the previous reading from the input pin
// the following variables are unsigned longs because the time, measured in
// milliseconds, will quickly become a bigger number than can be stored in an int.
unsigned long lastDebounceTime = 0; // the last time the output pin was toggled
unsigned long debounceDelay = 50; // the debounce time; increase if the output flickers
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// set initial LED state
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
}
void loop() {
// read the state of the switch into a local variable:
int reading = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// check to see if you just pressed the button
// (i.e. the input went from LOW to HIGH), and you've waited long enough
// since the last press to ignore any noise:
// If the switch changed, due to noise or pressing:
if (reading != lastButtonState) {
// reset the debouncing timer
lastDebounceTime = millis();
}
if ((millis() - lastDebounceTime) > debounceDelay) {
// whatever the reading is at, it's been there for longer than the debounce
// delay, so take it as the actual current state:
// if the button state has changed:
if (reading != buttonState) {
buttonState = reading;
// only toggle the LED if the new button state is HIGH
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
ledState = !ledState;
}
}
}
// set the LED:
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
// save the reading. Next time through the loop, it'll be the lastButtonState:
lastButtonState = reading;
}
Comments
Post a Comment